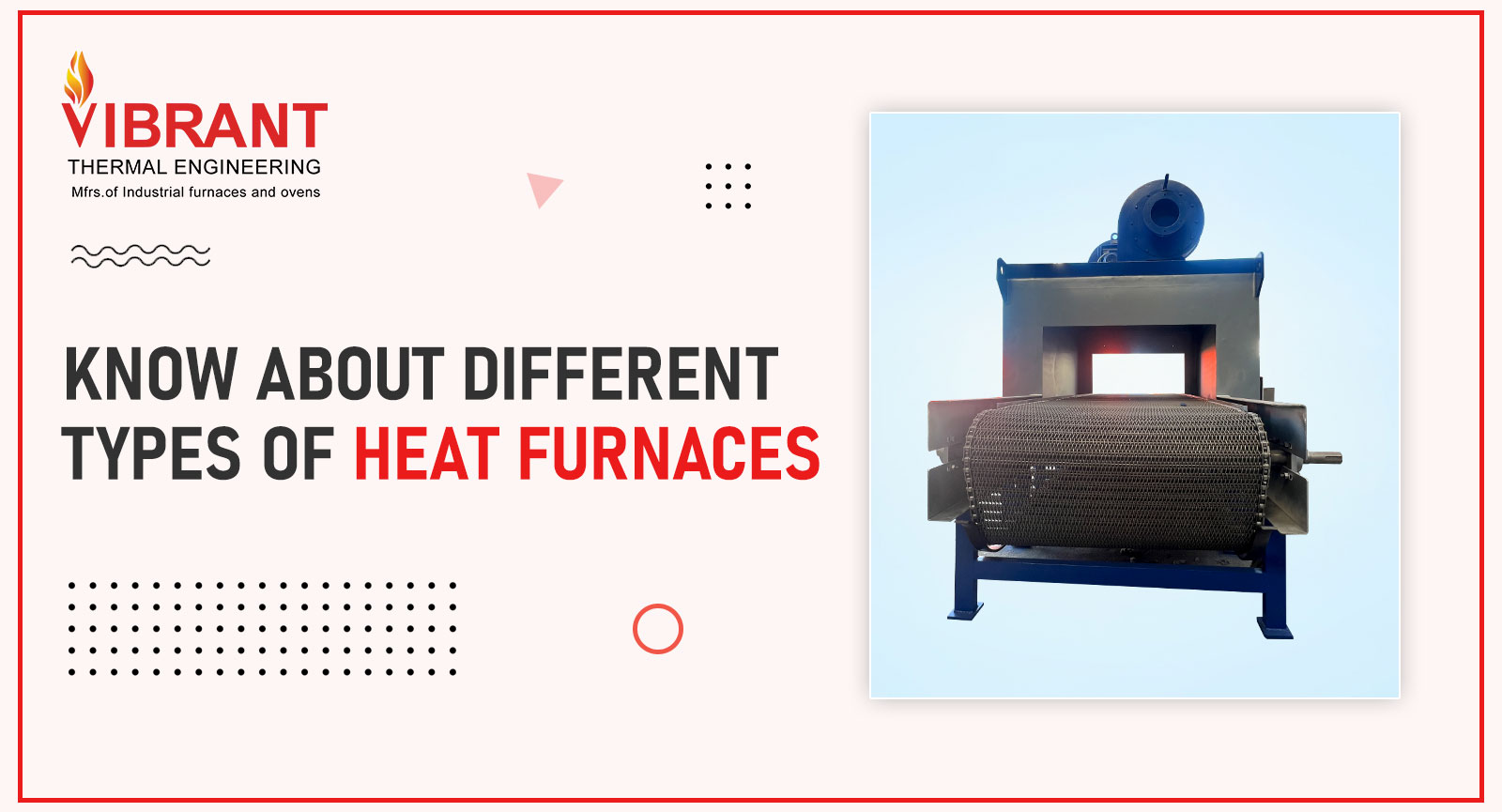
Most labs and industrial facilities use a heat treatment furnace in their daily operations, making it a vital piece of equipment in the workplace. Heat treatment furnaces are effective and adaptable equipment for high-temperature heating and convection. These furnaces are available in a variety of forms and combinations, each tailored to a specific application. Some of them include batch and continuous furnaces.
If you are thinking about purchasing a heat-treatment furnace, you should know which type to acquire and which one will meet your demands. Continue reading to learn about the many types of heat furnaces.
Continuous furnaces provide a continuous flow of workpieces through the heating chamber via a conveyor or roller system. The furnace’s heating components create the necessary heat, and the conveyor system assures a consistent flow of workpieces through the heating chamber. As the workpieces pass through the furnace, they go through the necessary heat treatment procedure.
Unlike Continuous Furnaces, batch furnaces use a single chamber for heating and cooling, known as the batch. The batch is stationary, so changes in the furnace atmosphere occur in near-equilibrium conditions. One frequent application for batch furnaces is to heat a collection of big, heavy components from room temperature to a particular set point before lowering them in a controlled way.
Contact Vibrant Thermal Engineering, immediately if you have any questions about furnace installation, maintenance, or repair. Don’t forget to inquire about our high-efficiency home heating systems to help you save money on your energy costs.
Types of Heat-Treatment Furnaces
Continuous Furnaces
Continuous furnaces, as the name implies, are industrial heat treatment furnaces that can accommodate a constant flow of workpieces. Unlike batch furnaces, which only handle a limited number of workpieces at a time, continuous furnaces provide a continuous and uninterrupted heat treatment procedure. They are suited for large-scale production and continuous heat treatment procedures.Continuous furnaces provide a continuous flow of workpieces through the heating chamber via a conveyor or roller system. The furnace’s heating components create the necessary heat, and the conveyor system assures a consistent flow of workpieces through the heating chamber. As the workpieces pass through the furnace, they go through the necessary heat treatment procedure.
Box/ Batch furnaces
Box furnaces, also known as batch furnaces, are flexible and commonly used for a variety of heat treatment operations. They are made up of an insulated chamber that can fit the workload while also providing regulated warmth. The box furnace’s primary function is to create a controlled heating environment for various heat treatment operations.Unlike Continuous Furnaces, batch furnaces use a single chamber for heating and cooling, known as the batch. The batch is stationary, so changes in the furnace atmosphere occur in near-equilibrium conditions. One frequent application for batch furnaces is to heat a collection of big, heavy components from room temperature to a particular set point before lowering them in a controlled way.
Natural Gas Furnace
The most prevalent form of furnace in today’s houses is a natural gas furnace, which connects to a municipal gas line and runs via central air ducts. Gas jets along a burner ignite to produce hot combustion gas, which elevates the temperature of the air and is subsequently circulated through the ducts by fans. When compared to other types of furnaces, gas heating is the most cost-effective since natural gas is often less expensive than oil and electricity.Natural Gas Furnace
The most prevalent form of furnace in today’s houses is a natural gas furnace, which connects to a municipal gas line and runs via central air ducts. Gas jets along a burner ignite to produce hot combustion gas, which elevates the temperature of the air and is subsequently circulated through the ducts by fans. When compared to other types of furnaces, gas heating is the most cost-effective since natural gas is often less expensive than oil and electricity.Oil Furnace
If you don’t have access to natural gas, you could have to fuel your furnace with oil. Oil furnaces are most typically utilized in cold areas, particularly in the northeastern United States. They convert oil to heat. While oil furnaces are less energy efficient than gas furnaces, they are still an effective way to heat your house.Electric Furnace
If you do not have a natural gas line running into your home, an electric furnace might be a great alternative. These systems employ electric heating elements to warm the air and distribute it throughout the house’s ducting. Electric furnaces are often less expensive to purchase upfront and smaller than traditional furnaces, making them easier to fit into most locations. Electric furnaces, like oil furnaces, are far less efficient, but they might be a good alternative if your options are restricted.Atmospheric furnace
During the heating and cooling operation, an atmosphere furnace surrounds the task with a “protective” environment. The most frequent furnace atmosphere is air. An air environment is commonly employed in low-temperature tempering processes. In this situation, visual appeal is usually unimportant since the air environment exposes the material to challenges such as oxidation, which affects its surface or skin.Choose the Perfect Heat Treatment Furnace.
A heating chamber or heat treatment furnace is required to complete tasks in different industries. As a result, you must select the appropriate type of furnace for your workplace or project. Check out our wide range of heat treatment furnaces including continuous furnaces.Contact Vibrant Thermal Engineering, immediately if you have any questions about furnace installation, maintenance, or repair. Don’t forget to inquire about our high-efficiency home heating systems to help you save money on your energy costs.